PLAY:double click STOP:one click Walking sensibly means taking every step thinking of the positive transformations and marks we left where we’ve been to and to those we related with. It means making sure changes are for better. It means investing on quality, seeking good results. It means commiting ourselves to leave a positive legacy where we’ve been to. Just as Ponto de Partida group tries to make its performances enchanting and inspiring, COPASA also endeavors to leave marks compatible to its desire to contribuie to a better future. Manifest of Nhá Terra (Regina Bertola) One shall care wells and water which feeds man’s dwelling. One shall care for fishes and rivers, nests and forests, seeds and fruits, flights and births, tiny beings and the ocean. One shall take hold of the energy offered by the sun and the winds. Nothing can become waste. All has to be recycled, recomposed, reinvented. One shall plant trees for long and protect the air so it is suitable for butterflies and boys. Do you promise to fulfill the requests from Nhá Terra?
Environmental responsibility In order to ensure quality sanitation to over 13 million Minas Gerais citizens, the Company is expanding its investments in preserving water resources in the State of Minas Gerais. COPASA preserves more than 24 thousand hectares of water stream preservation areas, ensuring continuity of public water supply with quality, and survival of hundreds of native fauna and flora species. In addition to water resources preservation actions, the Company prioritizes sewage treatment works in the cities where it operates, and undertakes decontamination actions by installing sewage systems – collection lines, interceptors, sewage pumping and treatment stations – in order to gradually reduce environmental impact from its operations. The Company promotes environmental education actions to make more conscious citizens, with relevant initiatives to combine economic development with respect to the environment and sustainability. In 2011, COPASA invested in the implementation of programs for environmental awareness, preservation and development, in payments related to usage of water resources, in processes of environmental licensing, used water source monitoring, among others, and as well projects and actions with focus on preserving the State of Minas Gerais water sources and on environmental sustainable practices. Not only essential to the future of mankind and the planet, care with natural resources is essential to COPASA, as they are critical to ensure the services under its responsibility have competitive and sustainable basis. Therefore, the Company continuously reassesses its work process, making its corporate activities compatible to the environment care and preservation.
ENVIRONMENTAL POLICY In June 2005, COPASA implemented its Environmental Policy, of which the principles are:
ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT The Company’s strategic planning entails an Environmental Management Policy and its guidelines. In 2005 the Company’s Administrative Counsil approved the implementation of an Environmental Management System in order to enable its fulfillment of the environmental policy and ensure its commitment with the environment. Since then, the system has allowed better cost control (specially waste of raw material, fuels and energy), and reduction of accidents, as well as facilitated the Company’s relationship with environmental agencies and financial institutions. The system for environmental aspects management from COPASA projects enables as well the identification of improvement opportunities, exceeding local requirements and focusing actions on plans which contribute to prevent impacts.
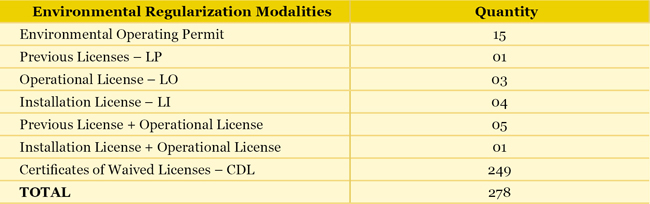
ENVIRONMENTAL LICENSING Previous environmental licensing is a requisite for the construction, installation, expansion and operation of sanitation works which use environmental resources and are considered effective or potentially polluting or prone to causing environmental degradation. The state legal basis for environmental licensing is Act 7772/80, under State Decree No. 39424/98. In the State of Minas Gerais, the agency responsible for environmental licensing and Environmental Operating Permit (AAF) is COPAM, State Council for Environmental Policies, through Regional Collegiate Units (URCs), Regional Environment and Sustainable Development Superintendence Offices (SUPRAMs), the State Foundation for the Environment (FEAM), the Water Management Institute from Minas Gerais (Igam) and the State Forest Institute (IEF). For the environmental regularization, the classification of projects is considered under the terms from Normative Resolution COPAM 74/04, which defines sizes of sanitation projects in its Annex I – listing E-03, according to the table hereunder:
For class 1 and 2 projects regarded as non-significant environmental impact, it is compulsory to obtain the Environmental Operating Permit (AAF). For the other classes (3 to 6), the path to environmental regularization is the licensing process, with the requests for Previous License (LP), Installation License (LI) and Operational License (LO). Following are the environmental regularizations implemented by the Company in 2011:
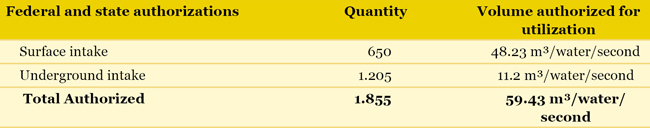
WATER RESOURCES COPASA has as its commitment and fundamental principle the respect and preservation of the environment and water resources, as established in its organizational principles and its Code of Ethical Conduct. National Policy of Water Resources The National Agency for Waters (ANA) is responsible to regulate its effectiveness, and ANA can delegate the power to grant rights of usage of federal water resources to states. Besides, Act 9433/97 acknowledges water as an economic asset, and so it aims to create conditions for balance between offer and demand, and to define billing for its use. However, for a billing to take place, it is necessary: to have in each drainage basin a Basin Committee installed and operating; to have a Basin Agency created and installed; to have an economic-financial feasibility study; that the Committee develops a Basin Plan, aiming to base and guide the implementation of programs and projects. State Policy of Water Resources The structure for billing of usage of water resource of state property is like federal billing. Its steps consist of installation and operation, in each drainage basin of a Basin Committee, creation and installation of a Basin Agency; performing an economic-financial feasibility study by the committee, and a Basin Plan aiming to base and guide the implementation of programs and projects. Water Intake In its main water intake activities, COPASA has authorization granted to use surface water sources (rivers, lakes or dams) or underground water. These authorizations are granted by the Water Management Institute from Minas Gerais (IGAM), for state-owned water sources, and by ANA for federal water sources. COPASA owns or has right to use land in intake areas from its water production systems. On December 31st, 2011, COPASA’s situation with respect to the right of using waters was:
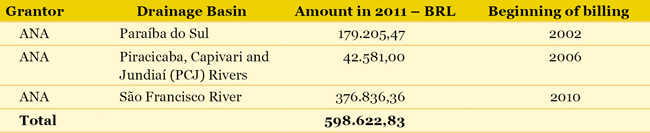
Note: on December 31st, 2011, there were 292 intake points of which the authorizations had already been requested or were under preliminary studies at the Company. Potable water supply at the metropolitan area of Belo Horizonte is under the Sistema Integrado (Integrated System) responsibility. This system consists of seven large sources, namely: Das Velhas River, Manso River, Serra Azul, Várzea das Flores, Morro Redondo, Ibirité and Catarina. Das Velhas river system is the largest individual water production system from COPASA, with an authorized flow rate of 8.77 l/s, which represents approximately 40% of the water supply thought the metropolitan area of Belo Horizonte. Payment for Utilization of Water Resources Billing for the water resource usage is a water management economic instrument considered in the National Policy of Water Resources and in the State Policy of Water Resources from Minas Gerais. This billing refers to using water resources subject to granted authorization, and aims to encourage rational water usage and to generate financial resources for investments in reinstatement and preservation of basin sources. The Company charges the users and passes on the amounts to the respective Basin Committees. Federal Basins
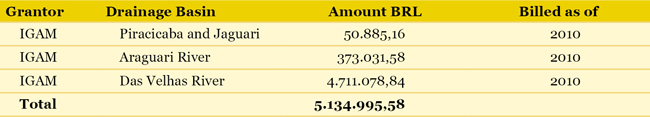
State Basins
Drainage Basin Management Committees The Drainage Basin Committees are deciding and rule-making bodies, in their operating territories, which aim to promote, with respect to water resource management, technical and economic-financial feasibility for the investment program and consolidation of urban and regional structure policies, seeking the basin sustainable development. The Basin Committees duties include, but are not limited to:
Creation of Basin Committees in the State of Minas Gerais must be made in accordance with Act 13199/99, which deals with the State Policy of Water Resources and with the state water division. It must be based on Water Resource Management and Planning units defined by the State Council of Water Resources.
Water Resource Management and Planning Units from the State of Minas Gerais
COPASA has representatives in 34 out of the 36 existing state Committees in the state of Minas Gerais and in four federal drainage basin Committees, and has been developing works in order to be represented in all of them. Its performance is based on the purpose of ensuring actions to promote reinstatement and preservation of the State water resources, making sure the Company has the conditions necessary to guarantee to the population from its authorized areas the access to good quality water at accessible prices. (GRI 4.13) In addition to the Committees, two basin agencies were settled in the state of Minas Gerais: Peixe Vivo and Multisector Association of Water Resource Users from Araguari River Drainage Basin (ABHA). These agencies are decentralized executive units which support their Drainage Basin Committees, with the purpose to give administrative, economic and technical support. ABHA is responsible to support the Araguari Committee (UPGRH PN2) and Peixe Vivo is responsible to support the Drainage Basins from Das Velhas River (UPGRH SF5), those surrounding Três Marias Dam (UPGRH SF4), from Pará River (UPGRH SF2) from Alto São Francisco branches (UPGRH SF1) and from Jequitaí and Pacuí rivers (UPGRH SF6).
Decontamination of Das Velhas River – 2014 Target (GRI SO5) One of the structure projects from the Government of the State of Minas Gerais undertaken by COPASA is Meta 2014 (2014 Target). Created in 2004 by Project Manuelzão, from the Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG), this project considers the reinstatement of Das Velhas River, by means of actions towards domestic and industrial sewage, reinstatement of riparian vegetation, and treatment of urban solid waste. In 2007, the Target has become one of the State’s structure projects. At first conceived as Target 2010, the commitment established was: navigate, fish and swim in Das Velhas River at the metropolitan area of Belo Horizonte (RMBH) in 2010. In August 2010, the Government of the State of Minas Gerais launched the project Meta 2014, which considers continuing actions from Structure Project Meta 2010, for the reinstatement of Das Velhas river drainage basin and its purpose is to get fish and swimming back to the metropolitan area of Belo Horizonte in 2014. The main actions are: selective collection and treatment of solid waste; collection, interception and treatment of domestic and industrial sewage in all municipalities from the RMBH and reinstatement of Pampulha lagoon. Getting fish back is the greatest indicator that the water quality has substantially changed. The Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG) found that in 2000 the fish would go only 250 km up river, and in 2007, they were identified at 470 km up river. The survey made in 2011 found fish at 714 km, which is upstream from the City of Belo Horizonte. In the period from 2004 to 2010, COPASA contracted more than 170 projects in the approximate amount of BRL 1.3 billion, with focus to modernization of the Arrudas Water Treatment Plant (ETE) and implementation of secondary treatment at Onça ETE, located in Belo Horizonte. The installations of ETEs head offices in São José da Lapa, and ETE Jardim Canadá, in the City of Nova Lima were completed; the ETE from 5P Basin, in Belo Horizonte; the ETEs from Pedro Leopoldo and Raposos; Veneza and Justinópolis, in the City of Ribeirão das Neves; the Central ETE, in the City of Santa Luzia; the ETE from Jaboticatubas; and the ETE Inácia de Carvalho, in São José da Lapa are under construction; plus improvements in ETE Sede, in Lagoa Santa. Besides, ETEs Pinhões, Casa Branca and ETE Tenente, in the city of Santa Luzia, and as well ETE Sede in Ribeirão das Neves, have engineering projects completed. After making the financial resources available, the works will be procured, and ETE Tenente will be procured in the first quarter of 2012. Another highlight is the works for removed of domestic sewage from Pampulha Lagoon, in Belo Horizonte, aiming at its decontamination by the World Soccer Cup of 2014. Another important job is the expansion of ETE Arrudas, of which the capacity of treatment will raise from 2.25 m³/s to 3,375 m³/s.
SEWAGE COLLECTION AND TREATMENT COPASA has been investing in sanitation infrastructure over the years, and in tune with the Government of the state of Minas Gerais it is performing the largest basic sanitation program ever made in the State. The Company has been seeking expansion of its coverage, with collection, interception of sewage and construction of new sewage treatment plants. ETE Areias: expected to start up in 2012, it is the largest ETE from Ribeirão das Neves, responsible for the treatment of sewage from approximately 240 thousand residents from the region of Justinópolis, or 60% of the population from the town of Ribeirão das Neves. Its operation will guarantee decontamination of various streams which run through this town and are part of Ribeirão da Mata basin, a branch from Das Velhas river. ETE Funilândia: expected to start up in 2012, ETE Funilândia will benefit 90% of the local population with sewage treatment. The project considers also the construction of 3.5 km of sewer lines and 480 building sewer tie-ins. With an estimated treatment flow rate of 6 l/s, the ETE will contribute with decontamination of Cabeceiras and Feijão streams, branches from Das Velhas river. ETE Guarda Mor: investments at the Company for the Development of São Francisco and Parnaíba Valleys (CODEVASF), which will contribute to decontamination of Ribeirão Guarda-Mor. This plant will be capable to treat 15.22 l/s, with 4,516 meters of sewer, to serve 4,006 residents. ETE Jaboticatubas: COPASA will take over in 2012 the operation of this town sewage collection and treatment, where a treatment plant is being constructed. ETE João Pinheiro: this plant will contribute to decontamination of Extrema stream and will be capable to treat 49.67 l/s, with 22,841 meters of sewer and 11,849 meters of interceptors, to serve a population of 32,980 residents. ETE Luizlândia do Oeste: job performed by the town of João Pinheiro. This plant will be capable to treat 14 l/s, with 16,558 meters of sewer, to serve 2482 residents. ETE Novo Retiro: this project covers sewer and interception lines, and is expected to serve 30% of the population from Esmeraldas, located in the region of Novo Retiro. With a flow rate of 50 l/s, this ETE operation will guarantee decontamination of Córrego Meloso, which is part of Paraopeba river basin. ETE Onça: with the startup of the second stage from Onça ETE, Belo Horizonte has become the first capital of the country capable to treat all its sewage at a secondary level. In 2011, ETE Onça flow rate grew 20%, specially due to treatment efficiency and implementation of works from Caça Esgoto Program. ETE Prudente de Morais: Agreement with Company for the Development of São Francisco and Parnaíba Valleys (CODEVASF) signed at the end of 2011. Design completed, under procurement phase, works will be started in 2012, expected to be completed in 18 months. ETE Raposos: within the expansion project for the city sewer, the construction work for the interception line and for a treatment plant is in progress and is expected to be completed in 2012. ETE Santa Luzia: with the construction of ETE Santa Luzia and the expansion of the system interception line, and works expected to be completed in 2012, this city, which hosts the third largest industrial center of Minas Gerais, will now have a system capable to handle collection and treatment of almost all the sewage from town. The construction of two more ETEs is expected for 2012, which will supplement the system and enable treatment of 100% of potential sewage. ETE Sede Esmeraldas: expected to start up in 2012, it will benefit, with sewage treatment services, the populations from the main neighborhoods around the City, which represent 15% of the total population. It will make all sewage be collected and treated before being returned to Nenêgo, João Paulo, Felipão and Raiz streams. ETE Veneza: this project will benefit about 80 thousand residents from Veneza region, and will contribute for decontamination of Ribeirão da Mata and therefore Das Velhas river. The works were stopped in 2011, awaiting new procurement. Some actions implemented in the metropolitan area of Belo Horizonte: Monitoring Program of Receiving Bodies Caça-Esgoto Program In 2011, the Caça-Esgoto Program completed the following works:
Program of Non-domestic Effluent Receiving and Control (PRECEND)
PRECEND has been growing skywards since its creation in 2003. In the beginning, 32 industries engaged, now there are more than 2,000 companies registered. In average, 40 technical projects are analyzed on a monthly basis. Out of the companies which completed the process, nearly 900 have a contractual obligation to submit to COPASA a report on how they self-monitor their effluents, as a way to verify compliance with the rule on effluent discharge at the public sewer system. The frequency in which the self-monitoring report is submitted is defined by COPASA, in accordance with the site size, its polluting potential, and risk at receiving its effluents. PRECEND receives an average of 270 self-monitoring reports a month.
ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION COPASA promotes environmental education, with the purpose to make individuals and the communities aware of how important water is for life. In this sense, the Company works towards recognition of all preservation areas under its responsibility as an everyone’s asset, making the population see its value and engage defense and protection actions towards its environmental integrity. CEAM Barreiro The socio-environmental actions performed are meant to make visitors see how important the area preservation is, by engaging them in environmental workshops and fun activities, and part of these activities is performed in direct contact with nature. An interpreting track is walked along the river side and part of the vegetation around the area. CEAM Barreiro is inserted in Project Sala Verde, from the Ministry of Environment, which aims to outline and develop educational activities towards the environment and to have a space defined and adapted for this purpose inside institutions. In 2011, CEAM Barreiro received around 4,800 visitors among students and teachers from 51 schools. CEAM ETE Arrudas The tour highlight is the biomonitoring system, an aquarium fed only by approximately 10 thousand liters of the liquid resulting from the plant sewage treatment. As it presents organic matter content much less than those determined by the environmental law, which proves the treatment quality and efficiency, it enables that different fishes found in Das Velhas river survive in this environment. There are also lectures about the environment, meant to promote environmental awareness. An exclusive channel of communication is made available for the ETE Arrudas neighboring community to inform any perception of odor to the plant operators. In addition , meetings are held with the community, for clarification about operational actions meant to minimize/eliminate bad odors. Around 1,300 people visited ETE Arrudas in 2001. Environmental Education Programs Water consumption education lecture Program Chuá for Sanitary and Environmental Education Through the Program Chuá for Sanitary and Environmental Education, COPASA maintains a relationship with educational institutes and the school public. The Program is held in hundreds of towns from Minas Gerais, operating for 25 years, has served over a million children and teenagers, contributing for the education of citizens more conscious and sensitive to environmental issues. The Program was developed with support from Regional Education Superintendence Offices, in order to serve the students and the community in a general manner. It offers learning material for teachers, students and representatives from other community segments, monitored tours at COPASA’s environmental reserves, water treatment plants, sewage treatment plants and environmental education centers. In addition to visits, there are lectures, and technicians from the Company teach basics about water and sewage treatment, conscious consumption, care with the environment, monitoring process for water treated by the Company in its laboratories, care with preservation areas, and others. In 2011, around 257 thousand people participated in the Program. Program of Tours of the Manso River System Project Vida Nova (New Life)
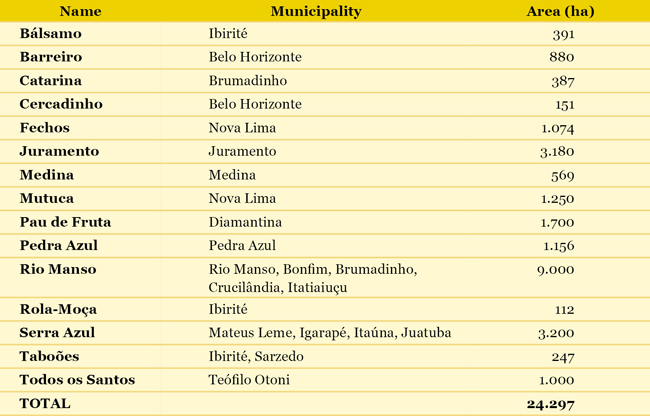
ENVIRONMENTAL PRESERVATION In order to preserve the Environment and ensure availability and quality of water resources, there are environmental preservation initiatives. State Park of Rola Moça The State Park of Rola Moça, with 3,941 hectares, covers the municipalities of Belo Horizonte, Nova Lima, Ibirité and Brumadinho, being considered one of the main green preserved areas from the metropolitan area of Belo Horizonte. Formed by a diversified vegetation, which includes transition vegetation of Rain Forest and Cerrado, in addition to unique ferrous fields, Rola Moça is managed by the State Forest Institute (IEF), together with COPASA, which also integrates the Council from this conservation unit. Environmental Reserves By preserving the environmental reserve areas, COPASA promotes flood control, mild climate in addition to biological and genetic balance. All of this ensures survival of all original fauna and flora. All the areas preserved by the Company have biological diversity, which shows its preservation level, hosting also threatened species. The table below shows the environmental reserves and their respective areas: (GRI EN11)
In addition to the State Park of Rola Moça, COPASA also participates of the consultative councils of Serra Verde and Lapa Grande State Parks, and the South and Carste lagoa Santa Environmental Preservation Areas. Protection of Water Sources Water Source Protection Program The Program aims to act gradually in all municipalities, at the sub-drainage basin upstream of COPASA intake, with the following environmental actions:
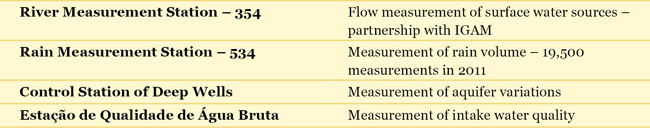
Through this Program, COPASA reinstates degraded areas by preventing erosion, eliminating pollution sources, recovering riparian vegetation and protecting river sources, that is, all actions favoring higher water availability during drought period and improvement of its quality. The program actions are developed and monitored by COPASA, and submitted for approval by farm owners, aiming particularly to establish commitment with the continuity of activities. With the approval, the Company’s technicians perform a verification of the property situation, in order to identify needs for environmental actions to be taken. In 2011, the Program operated in farms from 30 towns. Monitoring Water Sources COPASA monitors its surface and underground water sources – about 1,500 sources in the cities operated by the company throughout the state of Minas Gerais. The data collected is stored in specific databases and is made available for reference in order to determine the hydrogeological and hydroclimatic characteristics from the various regions of Minas Gerais. The monitoring program entails:
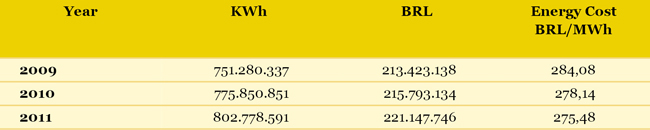
ENERGY CONSUMPTION AND ENERGY EFFICIENCY COPASA follows up and controls electric energy to be purchased in private and free markets, from self-production and energy efficiency actions, including control and elimination of actual water loss, the main opportunity to reduce specific consumption of electric energy. With these activities, the Company has obtained gains in standardizing actions to reduce electric energy costs and water loss, and as well in using self-production opportunities from energy available in sewage treatment process and in water accumulation dams. The energy efficiency projects aim to achieve less consumption of energy with lower costs, without prejudice to the excellent quality of services rendered to the society, by means of integrated and modern actions, with centralized and participative action, in perfect tune with the sector guidelines and with the international policies towards preservation of natural resources, quality of life improvement and environmental conditions. COPASA maintains the Integrated Program for Reduction of Water Loss and Electricity Costs, the so-called Energy Efficiency Program (PEE), which introduced actions towards rationing electricity usage, with basis on concepts and guidelines from the National Program Against Water Waste (PNCDA), from the International Water Association (IWA), from resolutions by National Agency of Electric Energy (ANEEL) and from the National Program for Conservation of Electric Energy in the Sanitation Sector (PROCEL SANEAR). The electric power consumption by COPASA in 2011 was 802,778,591 kWh.The indicator Energy Not Converted into Results (ENCR) expresses the quantity of energy added to the water volume not converted into revenue, as established by the Energy Efficiency Program (PEE), and shows the result from energy efficiency actions towards reduction of water loss. Evolution of Electric Energy Use in COPASA (invoicing data)
Sustainable Energy COPASA walks the path of sustainable energy investing in a thermoelectric plant, capable to transform high polluting methane gas from sewage treatment into energy. In 2011, the Company started the experimental operation of thermoelectric plant at the ETE from Ribeirão Arrudas basin. The power from this thermoelectric plant is 2.4 MW. The heat resulting from electric power production in the turbines also heats the silt used in the anaerobic reaction and increases the efficiency of biodigestors, which accelerates work and increased the current ETE capacity. Besides, COPASA performed a Clean Development Mechanism (MDL) related to reduction of greenhouse gas emission resulting from the thermo plant installation. The steps of public consulting and project validation were taken, which considers reduction of 26,237 tCO2e (equivalent carbonic gas tons) for the certification period.
INCENTIVE TO CONSCIOUS CONSUMPTION AND REUSE OF MATERIALS With an eye on the destination of waste generated in its facilities, COPASA has implemented the concept and culture of selective collection among employees over the years. This process started with paper collection by installing customized bins in organizational units located in the city of Belo Horizonte. Then, the procedure has expanded to other company’s units. There are individual and group bins for paper, metal, glass, plastic and non-recyclable waste, in addition to battery bins. In Belo Horizonte, the materials collected are donated to the Association of Paper, Cardboard and Reusable Material Collectors (Asmare), and the approximate monthly volume is 5 tons. COPASA also contracts companies specialized in collection, transportation and decontamination of burnt out, fluorescent and multi-vapor light bulbs, aiming at the ecologically correct destination. Besides, it maintains a partnership with philanthropic institutions for recyclable material collection, like: paper, cardboard, magazines, newspapers, aluminum cans, plastic bottles, etc. The Company implemented a technological solution which allows rationalization and modernization of document management, the Electronic Documents Management (GED). The system, in addition to transforming hard files in electronic files, provides quick access, safety and reduction of costs with inputs like paper, ink, mail, transportation, and others. With a search system, a registered user can access and consult documents without need to print them.
CLIMATE CHANGES Inventory of Greenhouse Gases COPASA does the inventory of GHG emissions generated in its activities, with the purpose to identify and quantify the main sources of GHG emissions in the Company. Results have shown that over 90% of COPASA emissions are a result from raw sewage discharge into the environment. The transportation of products, goods, materials and workers has shown as accountable for less than 3% of emissions. The increase in the treated sewage portion in relation to the total sewage collected and the increase of the treated sewage portion in composite and aerobic plants causes a reduction of GHG emissions, therefore the tendency is that those emissions have a gradual reduction over the next years. The results from this study were stated in the Program for Volunteered Registration of Annual Emission of GHG from sites in the state of Minas Gerais, and in the Carbon Disclosure Project. |
||